 Home
Home
 Back
Back
This calculator determines a safe starting dose of gabapentin (Neurontin) based on indication and age, using these guidelines:
Typical Daily Dose (mg):
Day 1: 300 mg/day | Day 2: 600 mg/day | Day 3+: 900 mg/day
Maintenance (Epilepsy/Restless Legs): 900–1800 mg/day
Dose per Administration (mg):
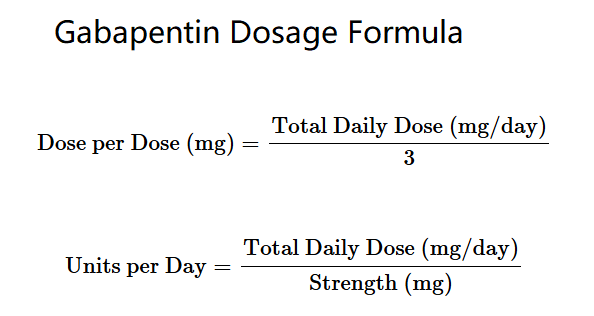
Dose per Dose (mg) = Total Daily Dose (mg/day) / 3 (Three Doses per Day after Day 2)
Units per Day (Capsules/Tablets):
Units per Day = Total Daily Dose (mg/day) / Strength (mg)
Where:
Dose starts at 300 mg on Day 1, increases to 600 mg on Day 2, and 900 mg on Day 3, given every 8 hours (3 doses/day) beyond Day 2. Maintenance may increase to 1800 mg/day for Epilepsy and Restless Legs. Maximum dose is 3600 mg/day.
This tool estimates a gabapentin dose based on indication and age. Select the indication (Epilepsy, Restless Legs Syndrome, Postherpetic Neuralgia, Peripheral Neuropathy, Anxiety), enter the patient’s age (default 18 years), and choose the drug type (Capsule 100 mg, 300 mg, 400 mg, or Tablet 600 mg, 800 mg). Results show the titration schedule, units per day, and maximum daily limit.
Example: Epilepsy, Age 18, Capsule 300 mg:
Titration Schedule (Every 8 hours after Day 1):
⁍ Day 1: 300 mg (1 dose) - 1.0 Capsules of 300 mg.
⁍ Day 2: 600 mg (2 doses) - 2.0 Capsules of 300 mg.
⁍ Day 3 and beyond: 3.0 Capsules of 300 mg.
⁍ Maintenance: 900–1800 mg per day .
You'll need 3.0–6.0 Capsules of 300 mg per day.
Do not exceed 3600 mg per day (1200 mg per dose).
Consult a healthcare provider before administering.
Gabapentin treats epilepsy (seizures), restless legs syndrome, postherpetic neuralgia, peripheral neuropathy, and anxiety (off-label).
Once on Day 1 (300 mg), twice on Day 2 (600 mg), then three times daily (every 8 hours) from Day 3 onward (900–1800 mg/day).
Not under 3 years for any indication, or under 12 years for restless legs, neuralgia, neuropathy, or anxiety. Epilepsy allows use from age 3.
Capsules (100 mg, 300 mg, 400 mg) and tablets (600 mg, 800 mg) are oral solids differing only in strength.
Duration varies by condition (e.g., chronic for epilepsy, short-term for neuralgia). Monitor for side effects like dizziness or sedation.