 Home
Home
 Back
Back
This calculator determines the maximum allowable subcutaneous (subQ) dose of lidocaine (without epinephrine) based on patient weight and concentration, using these guidelines:
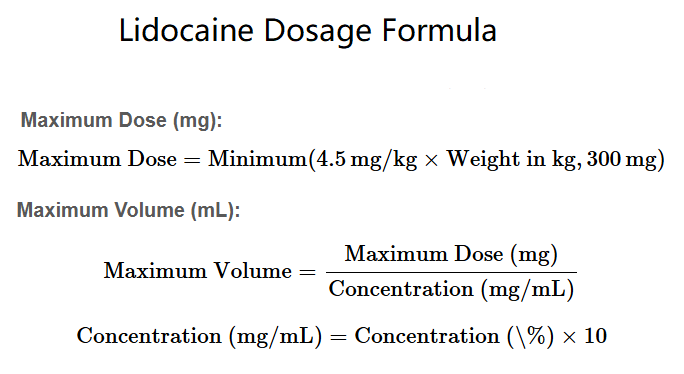
Maximum Dose (mg):
Maximum Dose = Minimum(4.5 mg/kg × Weight in kg, 300 mg)
Maximum Volume (mL):
Maximum Volume = Maximum Dose (mg) / Concentration (mg/mL)
Concentration (mg/mL) = Concentration (%) × 10
Where:
The maximum single dose of lidocaine without epinephrine is 300 mg, and the maximum subQ dose is 4.5 mg/kg.
This tool estimates the maximum allowable subcutaneous dose of lidocaine (without epinephrine) for local anesthesia. Enter the patient’s weight (kg) and select the lidocaine concentration (0.25%–4%). Results show the maximum volume (mL), dose (mg), and a warning about the single-dose limit of 300 mg.
Example: Weight 25 kg, Concentration 0.25%:
Lidocaine Dose Calculation:
Patient's Weight: 25.0 kg
Concentration: 0.25% (2.5 mg/mL)
Max allowable subQ dose, mL: 45.0 mL
Max allowable subQ dose, mg: 112.5 mg
⚠️ This tool is for information purposes only...
Consult a healthcare provider before administering.
Lidocaine is a local anesthetic used for numbing areas during procedures, without epinephrine for subQ administration in sensitive patients.
It’s based on weight (max 4.5 mg/kg) and concentration, with a single-dose limit of 300 mg without epinephrine.
Yes, but dosing must be weight-based and monitored closely, with pediatric guidance from a healthcare provider.
Concentrations range from 0.25% (2.5 mg/mL) to 4% (40 mg/mL), affecting the volume needed for the same dose.
Exceeding 300 mg or 4.5 mg/kg can cause toxicity (e.g., seizures, cardiac issues). Always consult a provider for safe dosing.